Deprecation
Why Would You Deprecate Datasets?
The Deprecation feature on DataHub indicates the status of an entity. For datasets, keeping the deprecation status up-to-date is important to inform users and downstream systems of changes to the dataset's availability or reliability. By updating the status, you can communicate changes proactively, prevent issues and ensure users are always using highly trusted data assets.
Goal Of This Guide
This guide will show you how to read or update deprecation status of a dataset.
Prerequisites
For this tutorial, you need to deploy DataHub Quickstart and ingest sample data. For detailed steps, please refer to Datahub Quickstart Guide.
Before updating deprecation, you need to ensure the targeted dataset is already present in your datahub. If you attempt to manipulate entities that do not exist, your operation will fail. In this guide, we will be using data from a sample ingestion.
Read Deprecation
- GraphQL
- Curl
- Python
query {
dataset(urn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_created,PROD)") {
deprecation {
deprecated
decommissionTime
}
}
}
If you see the following response, the operation was successful:
{
"data": {
"dataset": {
"deprecation": {
"deprecated": false,
"decommissionTime": null
}
}
},
"extensions": {}
}
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/api/graphql' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <my-access-token>' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{ "query": "{ dataset(urn: \"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_created,PROD)\") { deprecation { deprecated decommissionTime } } }", "variables":{} }'
Expected Response:
{
"data": {
"dataset": {
"deprecation": { "deprecated": false, "decommissionTime": null }
}
},
"extensions": {}
}
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/dataset_query_deprecation.py
from datahub.emitter.mce_builder import make_dataset_urn
# read-modify-write requires access to the DataHubGraph (RestEmitter is not enough)
from datahub.ingestion.graph.client import DatahubClientConfig, DataHubGraph
# Imports for metadata model classes
from datahub.metadata.schema_classes import DeprecationClass
dataset_urn = make_dataset_urn(platform="hive", name="fct_users_created", env="PROD")
gms_endpoint = "http://localhost:8080"
graph = DataHubGraph(DatahubClientConfig(server=gms_endpoint))
# Query multiple aspects from entity
result = graph.get_aspects_for_entity(
entity_urn=dataset_urn,
aspects=["deprecation"],
aspect_types=[DeprecationClass],
)
print(result)
Update Deprecation
- GraphQL
- Curl
- Python
mutation updateDeprecation {
updateDeprecation(input: { urn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_created,PROD)", deprecated: true })
}
Also note that you can update deprecation status of multiple entities or subresource using batchUpdateDeprecation.
mutation batchUpdateDeprecation {
batchUpdateDeprecation(
input: {
deprecated: true,
resources: [
{ resourceUrn:"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hdfs,SampleHdfsDataset,PROD)"} ,
{ resourceUrn:"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_created,PROD)"} ,]
}
)
}
If you see the following response, the operation was successful:
{
"data": {
"updateDeprecation": true
},
"extensions": {}
}
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/api/graphql' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <my-access-token>' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{ "query": "mutation updateDeprecation { updateDeprecation(input: { deprecated: true, urn: \"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_created,PROD)\" }) }", "variables":{}}'
Expected Response:
{ "data": { "removeTag": true }, "extensions": {} }
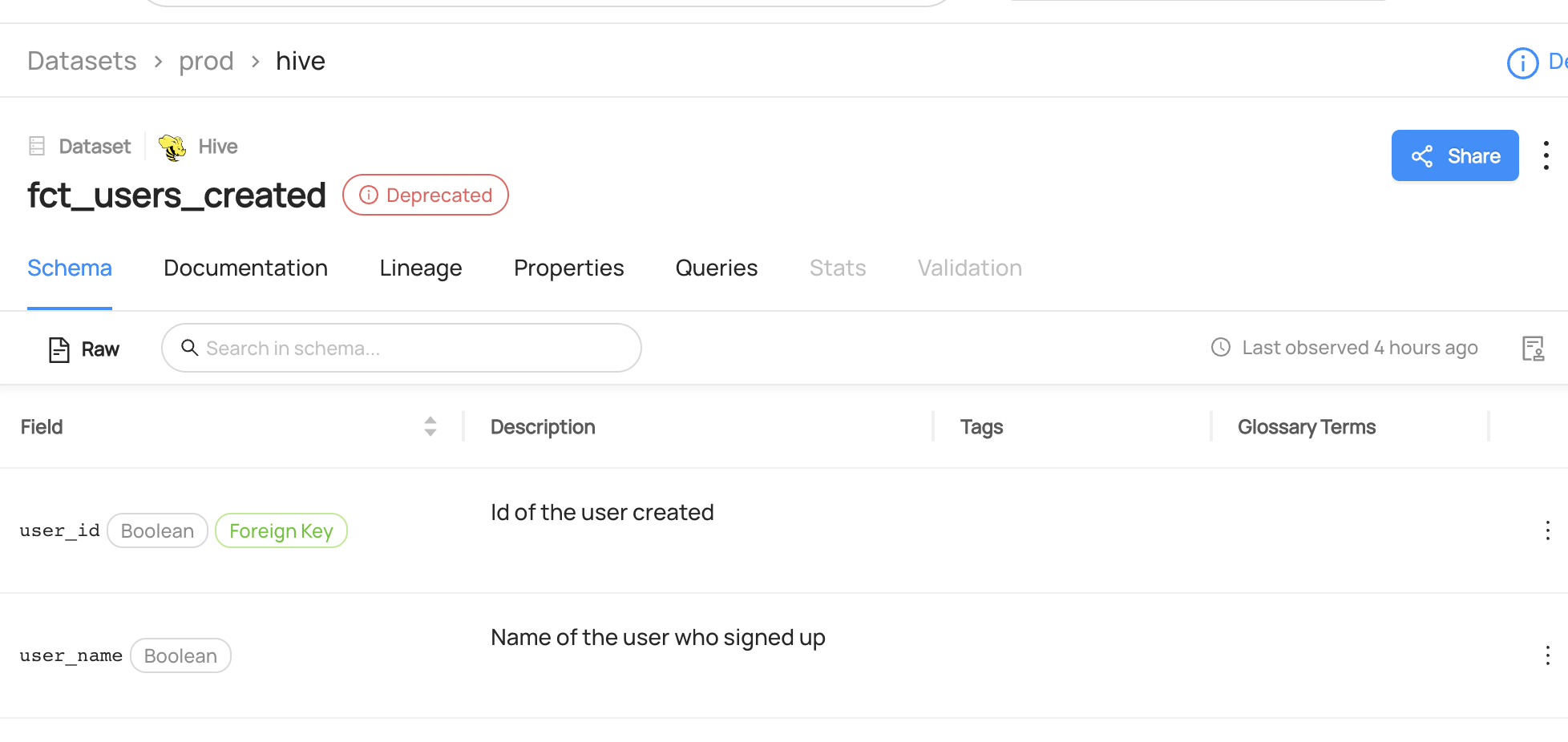
Expected Outcomes of Updating Deprecation
You can now see the dataset fct_users_created has been marked as Deprecated.